Premenstrual food cravings are the punchline of endless jokes. Like most good jokes, they’re funny because they’re true.
Craving and eating before a period
Food cravings are just one of the many symptoms of premenstrual syndrome, also known as PMS. PMS is likely caused by hormonal fluctuations and how they affect chemical messengers in the brain called neurotransmitters. Its symptoms are exclusive to the second half of the menstrual cycle.
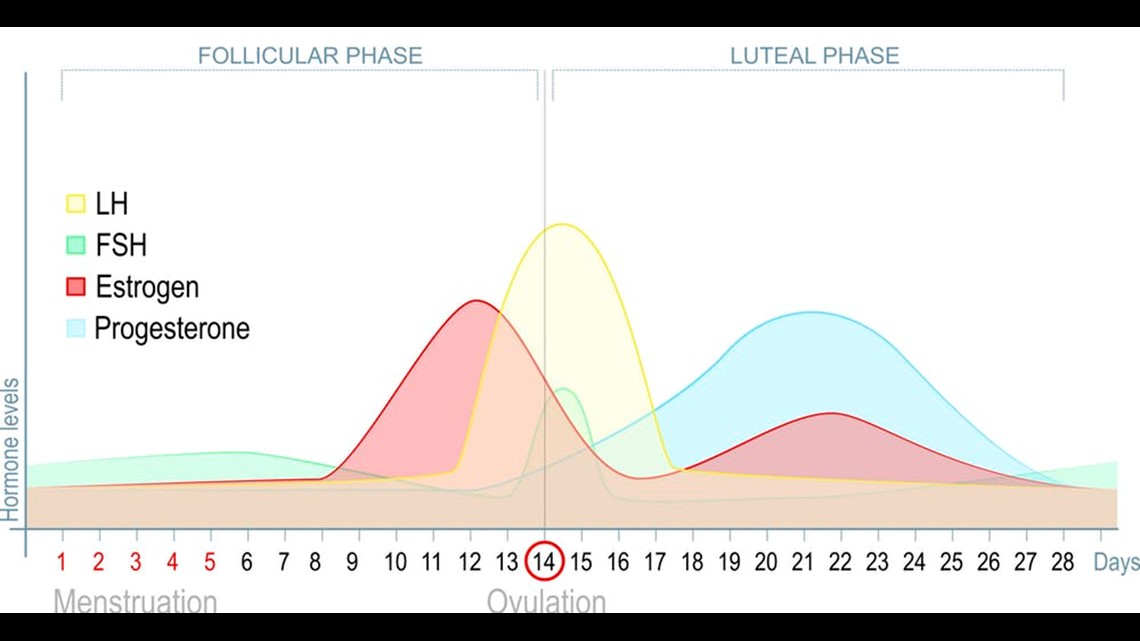
This luteal phase of the cycle starts with the release of the egg at ovulation and ends when a period begins. The symptoms usually resolve around the third or fourth day of menstruation.

Researchers have documented more than 150 different PMS symptoms in studies, ranging from physical to emotional to behavioral to cognitive. Food cravings are up there with the most commonly reported behavioral PMS symptoms, along with mood swings, irritability, anxiety and tension, and sad or depressed mood.
A woman doesn’t need an official diagnosis of PMS to report hankering for sweets and chocolates, though. Eighty-five percent of women have some sort of perceptible premenstrual symptoms, while only somewhere in the range of 20% to 40% of all women meet the diagnostic criteria for PMS.
Researchers find that cravings can occur during that premenstrual time period in normal, healthy individuals without a diagnosis of PMS or other disorder. In fact, one study showed that 97% of all women had previously experienced food cravings – independent of their menstrual cycle.
Research data confirm women tend to eat more during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared to the follicular phase that leads up to ovulation. With or without the diagnosis of PMS, this increased food intake can be as high as 500 extra calories per day.
What foods are women reaching for? Carbs and fats and sweets. No surprise there. The most commonly reported food craving is chocolate, likely because it’s a pleasantly sweet combination of carbs and fat.
And although the existence of any craving is similar across women with and without PMS, the craving itself may differ depending on if you have the diagnosis of PMS. In one study, women without PMS increased their intake of energy and fat, while women with PMS showed increase in total energy and all macronutrients.
What causes food cravings?
Researchers aren’t exactly sure where these food cravings come from, but there are several leading theories.
One idea is that women are unconsciously using food as a pharmacological therapy. Many studies show that women in their luteal phase crave more carbohydrates compared to during their follicular phase. Eating carbs turns up levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, which contributes to a general sense of well-being and happiness.
By increasing carb intake, women may be self-medicating with food to cause that serotonin bump in order to feel better. In one study, when researchers increased serotonin neurotransmission in the brain, either through diet or drugs, people’s food intake and mood went back to normal.
Another possible explanation for food cravings suggests that women intentionally turn to food for physical and psychological comfort. Food can play a sensory role, eliminating any uncomfortable feeling of hunger while tasting good and feeling pleasant to eat. Researchers find that “thinking” of a really tasty food is the most common provocation for wanting to consume it and that cravings are not solely hunger driven.
Women also usually reported specific triggers for thinking of comforting food, like boredom or stress, further promoting the idea that the comfort of food helps mitigate unpleasant feelings – as one might experience with PMS.
Other researchers suggest that these food cravings are regulated by hormones. Scientists have observed that women tend to eat more when estrogen levels are low and progesterone levels are high – as occurs during the luteal phase.
The reverse pattern is seen in rats during the follicular phase, when estrogen levels are high and progesterone levels are low. The fact that progesterone-only forms of contraception like Depo Provera are associated with weight gain, likely due to increased appetite, supports this theory as well.
How can you get rid of monthly cravings?
My general advice to women: be knowledgeable about your own body and how it changes in response to your monthly cycle. Your experience is different than your best friend’s. Being in touch with your symptoms can help you acknowledge that they are normal for you at this point in time instead of worrying whether they’re weird. If you feel unsure, ask your gynecologist.
- Choose complex carbohydrates, including whole grains, brown rice, barley, beans and lentils. Choose whole wheat over white flour.
- Reduce fat, salt and sugar – all of which can leave you craving more.
- Minimize or avoid caffeine and alcohol.
- Eat more calcium-rich foods, including green leafy vegetables and dairy. One study showed women who consumed milk, cheese and yogurt had less abdominal bloating, cramps, appetite and cravings for some foods, possibly because the calcium they contain helped reverse an imbalance of feel-good serotonin. Women who are sensitive to dairy can take a calcium supplement of 1200 mg daily.
- Try magnesium supplements. This mineral can help reduce water retention and bloating, breast tenderness and mood symptoms.
- Vitamin B6 (50 mg daily), in addition to magnesium, may have some benefit as well.
- Vitamin E (150-300 IU daily) may be helpful to reduce cravings.
When food cravings are part of a PMS diagnosis, treatment for premenstrual syndrome in general may help minimize them.
Dr. Sara Twogood is Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology, University of Southern California. This article is from The Conversation, a nonprofit news source dedicated to spreading ideas from experts. Republished under a Creative Commons license.